Can Eye Doctors Detect Brain Tumors? A Comprehensive Guide
Can an eye doctor detect a brain tumor? This question has been gaining attention as more people become aware of the connection between eye health and neurological conditions. While eye doctors, or ophthalmologists, are not neurologists, their specialized training equips them to identify certain symptoms that may point to underlying brain-related issues. Understanding the role of eye exams in detecting brain tumors can be a life-saving piece of knowledge. This article dives deep into how eye doctors contribute to early detection, the symptoms they look for, and the importance of regular eye check-ups.
Brain tumors can affect vision in various ways, and these changes often manifest in the eyes before other symptoms appear. This makes routine eye exams not only essential for maintaining good eye health but also for catching potential neurological issues early. An eye doctor’s ability to detect subtle changes in vision can sometimes lead to the discovery of a brain tumor before it progresses. In this article, we will explore the mechanisms behind this process, the specific signs an eye doctor might notice, and how this knowledge can empower patients to take control of their health.
Early detection of brain tumors is crucial because it can significantly improve treatment outcomes and survival rates. While brain tumors are relatively rare compared to other health conditions, their impact can be devastating if left untreated. Eye exams can serve as an unexpected yet effective diagnostic tool in these cases. By understanding the connection between eye health and brain health, individuals can make informed decisions about their medical care. Let’s delve into the details of how eye doctors play a vital role in detecting brain tumors and why this information is so critical.
- Yes King Original Video
- Patrick Mahomes Sr
- Movierulz Telugu Movies 2024 Page
- Shane Dawson Cat
- Tiktok Nip Slips
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Brain Tumors and Eye Health
- The Role of Eye Doctors in Detecting Brain Tumors
- Symptoms Eye Doctors Notice
- Diagnostic Tools Used by Eye Doctors
- How Brain Tumors Affect Vision
- Case Studies: Real-Life Examples
- Preventive Measures and Regular Check-Ups
- Collaboration Between Eye Doctors and Neurologists
- The Importance of Early Detection
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Brain Tumors and Eye Health
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the brain. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can occur in various parts of the brain. While the exact cause of brain tumors is often unknown, factors such as genetics, exposure to radiation, and certain environmental influences may increase the risk. One of the lesser-known but critical aspects of brain tumors is their potential impact on vision. The brain and eyes are intricately connected, and any disruption in the brain can manifest as changes in vision.
Eye health is an essential component of overall well-being, and regular eye exams are vital for maintaining it. During these exams, eye doctors assess not only the clarity of vision but also the health of the eye’s structures. This includes examining the retina, optic nerve, and other components that can provide clues about systemic health. For example, conditions like diabetes and hypertension often show early signs in the eyes. Similarly, brain tumors can affect the optic nerve or the pathways that transmit visual information to the brain, leading to noticeable symptoms during an eye exam.
Understanding the connection between brain tumors and eye health is crucial for early detection and intervention. While not all vision changes are indicative of a brain tumor, certain symptoms warrant further investigation. By being aware of these signs and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their chances of catching a brain tumor early. This section will explore the basics of brain tumors, their potential effects on vision, and why eye exams are an essential part of monitoring overall health.
The Role of Eye Doctors in Detecting Brain Tumors
Eye doctors, particularly ophthalmologists, are trained to evaluate not just the eyes but also the visual pathways that connect the eyes to the brain. This expertise allows them to identify abnormalities that may indicate underlying neurological conditions, including brain tumors. During a comprehensive eye exam, an ophthalmologist examines the retina, optic nerve, and other structures that can reveal signs of pressure or damage caused by a tumor. For instance, swelling of the optic disc, known as papilledema, is a common indicator of increased intracranial pressure and may suggest the presence of a brain tumor.
One of the key tools used by eye doctors is a dilated eye exam. This procedure involves using special eye drops to widen the pupil, allowing the doctor to examine the back of the eye in detail. During this exam, the doctor can detect changes in the optic nerve or retina that may not be visible during a routine check-up. Additionally, advanced imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus photography can provide detailed images of the eye’s structures, helping to identify abnormalities that may require further investigation.
Eye doctors also play a critical role in referring patients to neurologists or other specialists when necessary. If a doctor identifies signs that suggest a brain tumor, they will typically recommend additional tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis. This collaboration between eye doctors and neurologists ensures that patients receive timely and accurate care. By acting as the first line of defense, eye doctors contribute significantly to early detection and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Techniques Used by Eye Doctors
- Dilated Eye Exam: Allows for a detailed view of the retina and optic nerve.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Provides high-resolution images of the eye’s structures.
- Fundus Photography: Captures images of the back of the eye for further analysis.
Symptoms Eye Doctors Notice
Eye doctors are trained to recognize a range of symptoms that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor. These symptoms often manifest as changes in vision or eye function, which can be detected during a routine eye exam. One of the most common signs is blurred or double vision, also known as diplopia. This occurs when the brain tumor affects the cranial nerves responsible for controlling eye movement, leading to misalignment of the eyes. Patients may also experience sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes, which can be a red flag for increased intracranial pressure.
Another symptom that eye doctors look for is papilledema, or swelling of the optic disc. This condition occurs when there is increased pressure within the skull, often caused by a brain tumor pressing on the optic nerve. During an eye exam, the doctor can observe this swelling using an ophthalmoscope, a tool that allows them to examine the back of the eye. Papilledema is a critical indicator that requires immediate attention, as it can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
In addition to these symptoms, eye doctors may notice other visual disturbances, such as peripheral vision loss or visual field defects. These changes can occur when a brain tumor affects the pathways that transmit visual information from the eyes to the brain. Patients may describe seeing “blind spots” or having difficulty with tasks that require peripheral awareness, such as driving. By identifying these symptoms early, eye doctors can help patients seek timely medical intervention, potentially saving their lives.
Diagnostic Tools Used by Eye Doctors
Eye doctors rely on a variety of diagnostic tools to assess the health of the eyes and identify potential signs of brain tumors. These tools range from basic clinical examinations to advanced imaging technologies, each playing a crucial role in detecting abnormalities. One of the most fundamental tools is the ophthalmoscope, which allows doctors to examine the retina and optic nerve in detail. By shining a light into the eye, the doctor can observe changes in the optic disc, such as swelling or discoloration, that may indicate increased intracranial pressure.
Another essential diagnostic tool is optical coherence tomography (OCT), a non-invasive imaging technique that provides cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT allows doctors to measure the thickness of the retina and detect subtle changes that may not be visible during a standard eye exam. This technology is particularly useful for identifying early signs of optic nerve damage, which can be caused by a brain tumor. Similarly, fundus photography captures detailed images of the back of the eye, enabling doctors to monitor changes over time and compare results from previous exams.
In some cases, eye doctors may recommend additional tests, such as visual field testing or electroretinography (ERG), to assess the function of the visual pathways. Visual field testing evaluates the patient’s peripheral vision, while ERG measures the electrical activity of the retina in response to light. These tests provide valuable insights into how well the eyes and brain are communicating and can help identify issues that may require further investigation. By using a combination of these tools, eye doctors can detect potential signs of brain tumors and ensure that patients receive the care they need.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina.
- Fundus Photography: Captures high-resolution images of the back of the eye.
- Visual Field Testing: Assesses peripheral vision and identifies blind spots.
How Brain Tumors Affect Vision
Brain tumors can have a profound impact on vision due to their proximity to the visual pathways and cranial nerves. The brain is responsible for processing visual information received from the eyes, and any disruption in this process can lead to noticeable changes in vision. One of the most common effects is blurred or double vision, which occurs when a tumor presses on the cranial nerves that control eye movement. This can result in misalignment of the eyes, making it difficult for patients to focus on objects or track movement.
Another way brain tumors affect vision is by causing peripheral vision loss or visual field defects. These changes occur when a tumor interferes with the pathways that transmit visual information from the eyes to the brain. Patients may describe seeing “blind spots” or having difficulty with tasks that require peripheral awareness, such as driving or reading. In some cases, the tumor may compress the optic nerve, leading to a condition known as optic neuropathy, which can result in permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Increased intracranial pressure is another factor that can impact vision. When a brain tumor grows, it can cause pressure to build up within the skull, leading to swelling of the optic disc, or papilledema. This condition can cause headaches, nausea, and vision changes, and it requires immediate medical attention to prevent further damage. By understanding how brain tumors affect vision, patients and healthcare providers can work together to identify potential issues early and take steps to address them.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples
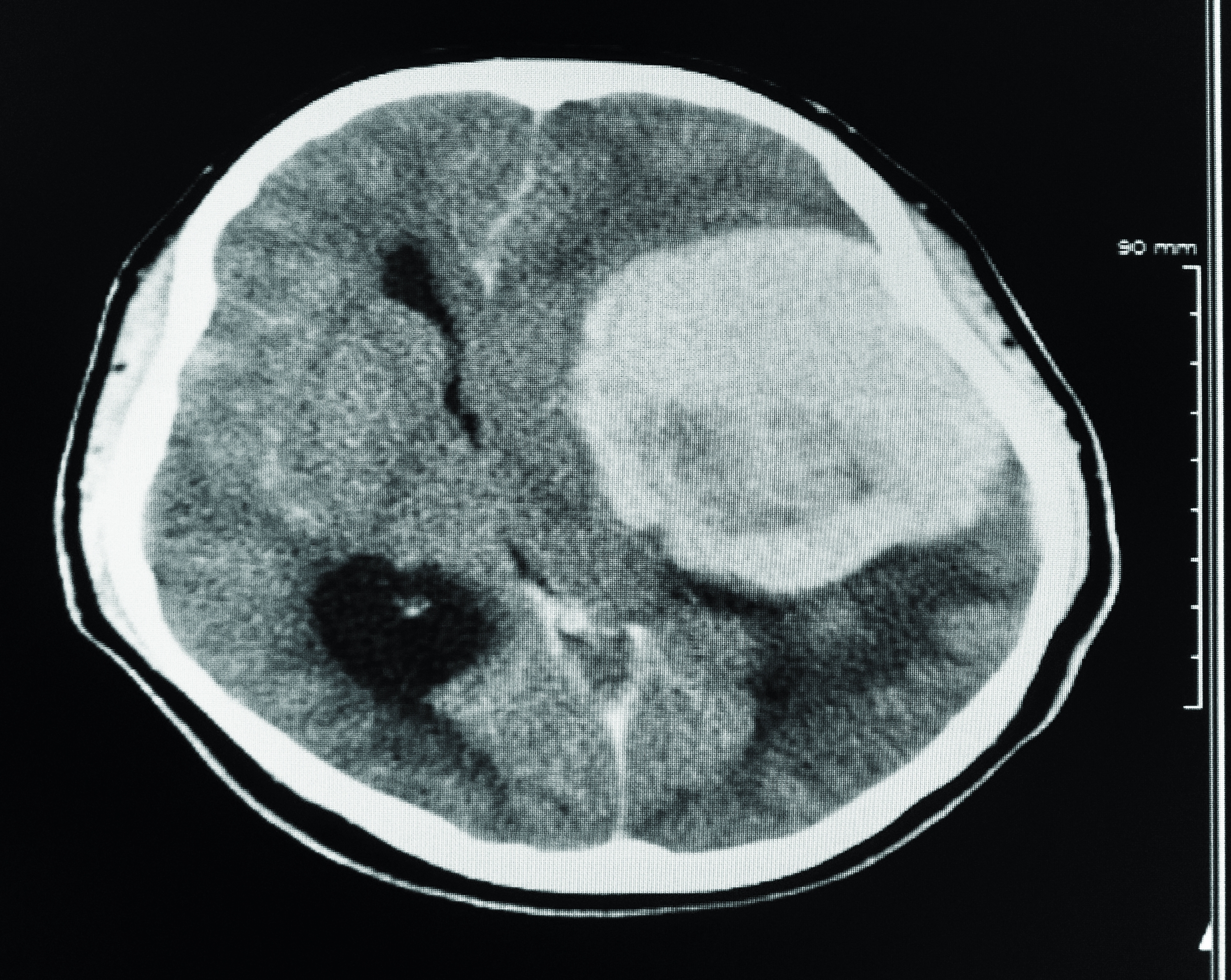
Real-life case studies provide valuable insights into how eye doctors have successfully detected brain tumors during routine exams. One notable example involves a 45-year-old woman who visited her ophthalmologist for a routine check-up. During the exam, the doctor noticed swelling of the optic disc, a condition known as papilledema. Concerned about the possibility of increased intracranial pressure, the doctor referred the patient to a neurologist for further evaluation. Subsequent imaging tests revealed a benign brain tumor, which was successfully removed through surgery. The patient’s vision returned to normal, and she continues to undergo regular follow-ups to monitor her health.
Another case involves a 30-year-old man who experienced sudden vision loss in one eye. He visited his eye doctor, who conducted a comprehensive exam and identified signs of optic nerve damage. The doctor immediately referred the patient to a neurologist, who ordered an MRI. The scan revealed a malignant brain tumor that was compressing the optic nerve. Thanks to the early detection and intervention, the patient underwent treatment that included surgery and radiation therapy. While his vision did not fully recover, the timely diagnosis prevented further complications and improved his overall prognosis.
These case studies highlight the critical role that eye doctors play in detecting brain tumors and ensuring timely medical intervention. By recognizing the signs and symptoms early, eye doctors can help patients receive the care they need, potentially saving their lives. These examples also underscore the importance of regular eye exams and the need for collaboration between eye doctors and neurologists to provide comprehensive care.
Preventive Measures and Regular Check-Ups
Preventing and managing the risk of brain tumors begins with proactive healthcare practices, including regular eye exams. While there is no guaranteed way to prevent brain tumors, early detection can significantly improve outcomes. Routine eye exams serve as an essential tool for monitoring overall health and identifying potential issues before they become severe. During these exams, eye doctors can detect subtle changes in vision or eye structure that may indicate underlying neurological conditions, such as brain tumors.
In addition to regular check-ups, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing brain tumors. Avoiding exposure to harmful radiation, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension can help lower the risk. It is also important to be aware of

Detail Author:
- Name : Marques Langworth
- Username : jlittle
- Email : heath94@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1994-12-06
- Address : 708 Kiley Squares Wunschborough, MO 10376-9777
- Phone : +1 (413) 292-3281
- Company : Robel, Streich and Hane
- Job : Sales Person
- Bio : Ipsa provident corporis rem. Asperiores necessitatibus sunt omnis autem voluptas consequatur optio. Eius nam est distinctio pariatur. Excepturi repellendus et laboriosam.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/heath_treutel
- username : heath_treutel
- bio : Optio magnam aliquam deleniti et et. Quod aut blanditiis amet labore omnis eligendi. Modi excepturi qui at magnam itaque.
- followers : 5135
- following : 276
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/heath.treutel
- username : heath.treutel
- bio : Dolorem quis eaque id quam eos qui. Aliquid molestiae est nemo aut eos tempore aut.
- followers : 6991
- following : 2654