Cantilever Retaining Walls: A Comprehensive Guide To Design, Construction, And Applications
Cantilever retaining walls are one of the most widely used structures in civil engineering and construction. These walls are designed to hold back soil or other materials, preventing erosion and creating usable space in areas with significant elevation changes. Whether you're a civil engineer, contractor, or homeowner planning a landscaping project, understanding the principles of cantilever retaining walls is essential for ensuring safety, functionality, and cost-effectiveness.
Retaining walls play a critical role in stabilizing slopes and preventing soil movement, making them indispensable in both urban and rural environments. Among the various types of retaining walls, cantilever retaining walls stand out due to their efficiency, durability, and adaptability. They are commonly used in highway construction, residential landscaping, and large-scale infrastructure projects.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about cantilever retaining walls, including their design principles, construction methods, advantages, and limitations. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how these walls work and how they can be applied to your projects. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Design Principles of Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Construction Methods and Materials
- Advantages of Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Limitations and Challenges
- Applications in Civil Engineering
- Maintenance and Longevity
- Cost Considerations
- Case Studies and Examples
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Cantilever Retaining Walls
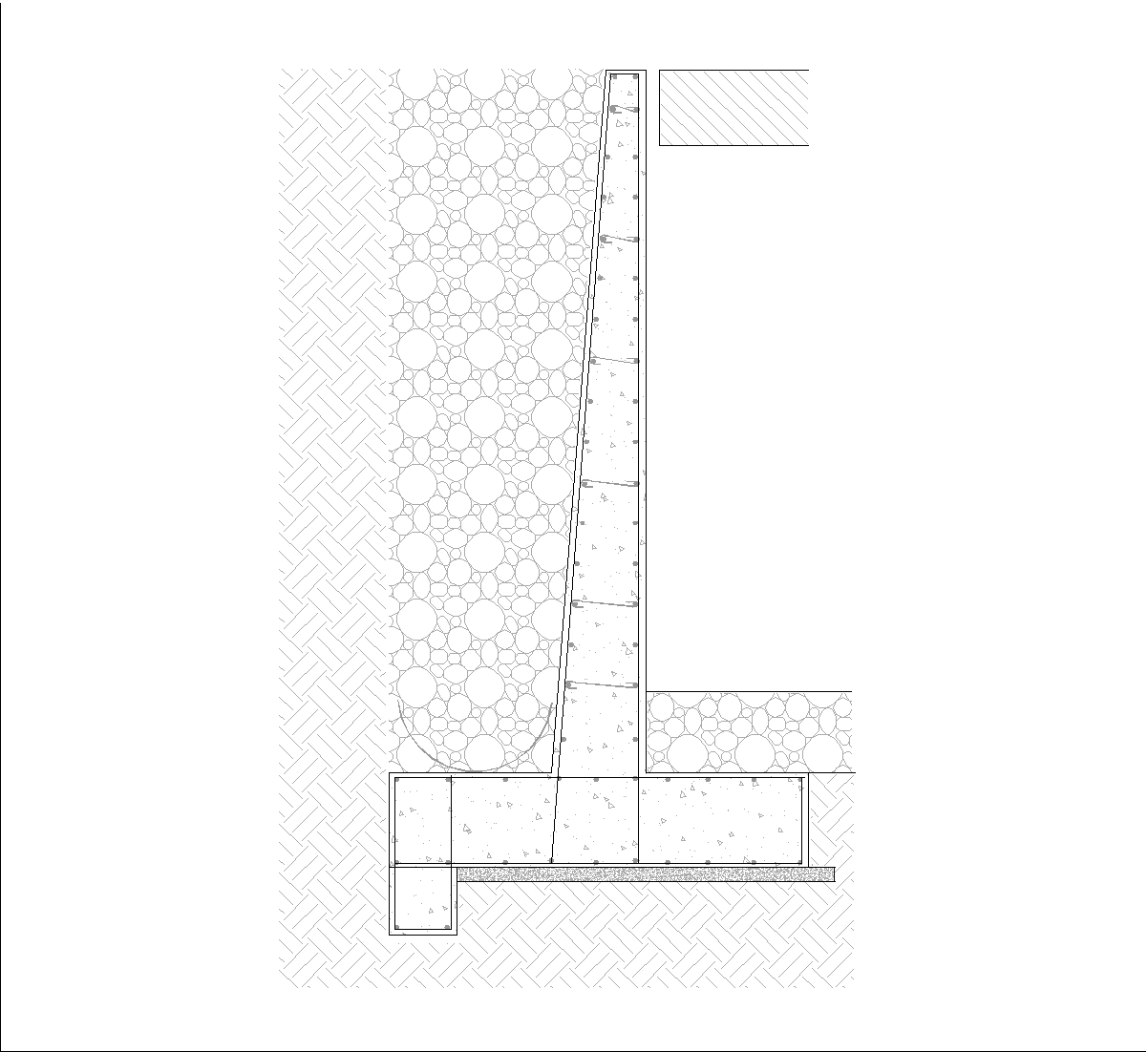
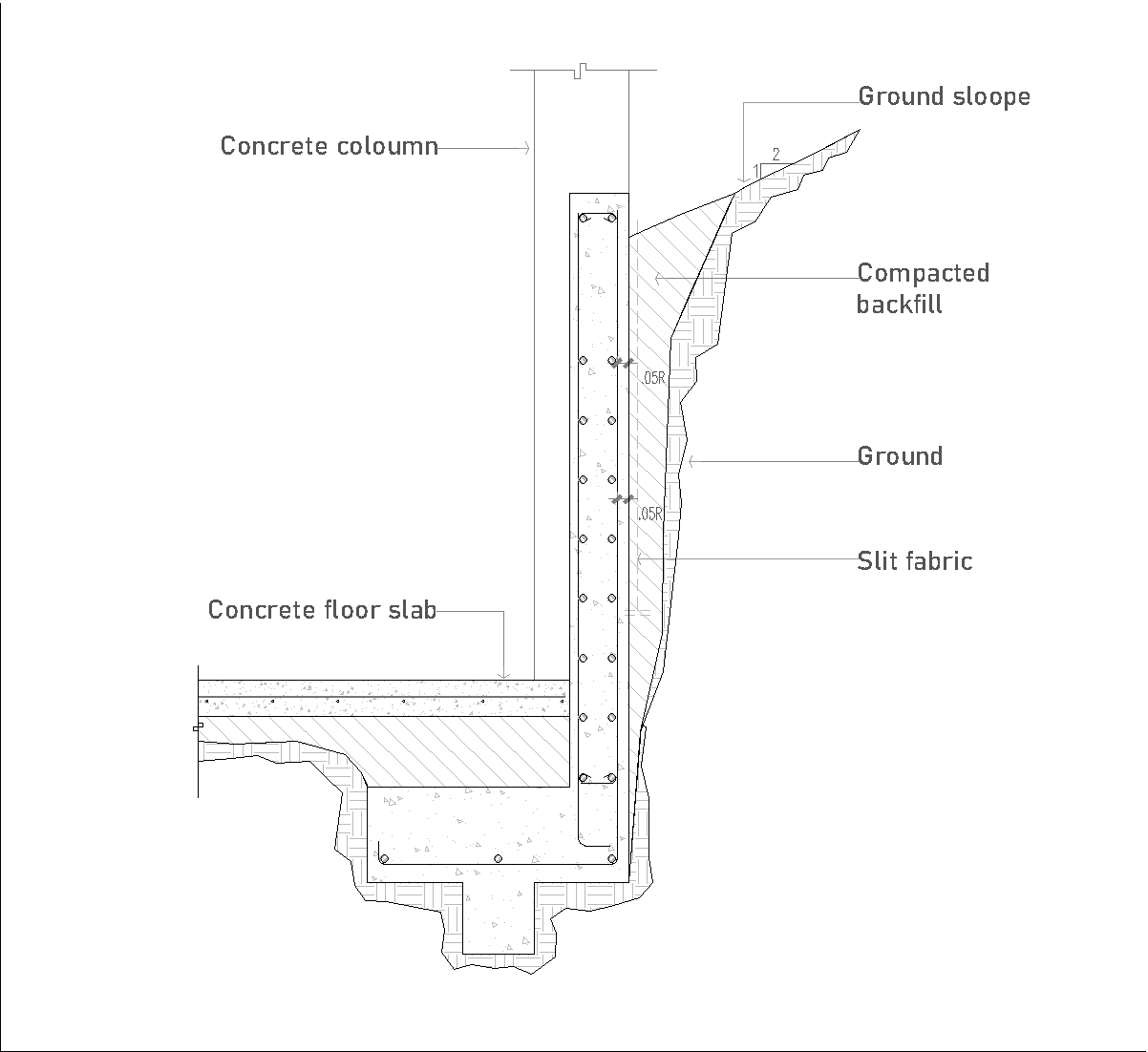
Cantilever retaining walls are structures designed to resist the lateral pressure of soil or other materials. They are called "cantilever" because they rely on a horizontal base slab and a vertical stem to distribute the load efficiently. This design allows the wall to resist overturning and sliding forces without requiring excessive material or reinforcement.
These walls are typically made of reinforced concrete, though other materials like masonry or steel can also be used. The cantilever design is particularly effective for heights ranging from 3 to 8 meters, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Key Components of Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Stem: The vertical portion of the wall that retains the soil.
- Base Slab: The horizontal foundation that provides stability and distributes the load.
- Toe: The front part of the base slab that extends outward.
- Heel: The rear part of the base slab that supports the retained soil.
Design Principles of Cantilever Retaining Walls
Designing a cantilever retaining wall requires careful consideration of various factors, including soil properties, wall height, and environmental conditions. Engineers must ensure that the wall can withstand lateral earth pressure, surcharge loads, and other forces.
1. Soil Mechanics and Lateral Pressure
The primary function of a retaining wall is to resist lateral earth pressure. This pressure depends on the type of soil, its angle of repose, and the presence of groundwater. Engineers use Rankine's or Coulomb's theory to calculate the lateral earth pressure and design the wall accordingly.
2. Structural Stability
Stability is achieved by ensuring that the wall can resist overturning, sliding, and bearing capacity failure. The base slab plays a crucial role in distributing the load and preventing excessive settlement.
3. Reinforcement and Materials
Reinforced concrete is the most common material for cantilever retaining walls due to its strength and durability. Steel reinforcement bars are embedded in the concrete to enhance tensile strength and prevent cracking.
Construction Methods and Materials
The construction of cantilever retaining walls involves several steps, from site preparation to final finishing. Each step requires precision and adherence to engineering standards to ensure the wall's longevity and performance.
Site Preparation
Before construction begins, the site must be cleared and leveled. Excavation is carried out to create a stable foundation, and drainage systems are installed to prevent water accumulation behind the wall.
Pouring the Base Slab
The base slab is poured first, ensuring that it is level and properly aligned. Reinforcement bars are placed according to the design specifications before the concrete is poured.
Erecting the Stem
Once the base slab has cured, the vertical stem is constructed. Formwork is used to shape the stem, and reinforcement bars are tied together to form a robust framework.
Advantages of Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever retaining walls offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for various applications:
- Economical: They require less material compared to gravity walls, making them cost-effective.
- Efficient: The cantilever design allows for taller walls with minimal material usage.
- Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of soil types and environmental conditions.
- Durable: Reinforced concrete ensures long-term performance with minimal maintenance.
Limitations and Challenges
While cantilever retaining walls are highly effective, they also have certain limitations and challenges:
- Height Restrictions: These walls are typically limited to heights of 8 meters or less.
- Complex Design: Requires expertise in structural engineering and soil mechanics.
- Foundation Requirements: A stable foundation is essential to prevent settlement and failure.
Applications in Civil Engineering
Cantilever retaining walls are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Highway Construction: To stabilize slopes and create level surfaces.
- Residential Landscaping: To create terraced gardens and prevent soil erosion.
- Commercial Projects: For parking lots, basements, and retaining structures.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity of cantilever retaining walls. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify cracks, settlement, or drainage issues. Timely repairs can prevent costly failures and extend the wall's lifespan.
Common Maintenance Tasks
- Inspecting for cracks or spalling in the concrete.
- Clearing drainage systems to prevent water buildup.
- Reinforcing weak areas with additional materials if necessary.
Cost Considerations
The cost of constructing a cantilever retaining wall depends on several factors, including wall height, materials, and site conditions. On average, the cost ranges from $50 to $150 per square foot. While the initial investment may be higher than other types of retaining walls, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs.
Case Studies and Examples
Let’s explore a few real-world examples of cantilever retaining walls in action:
Case Study 1: Highway Embankment Stabilization
In a highway project in California, cantilever retaining walls were used to stabilize steep slopes and prevent soil erosion. The walls successfully withstood heavy rainfall and seismic activity, proving their durability and reliability.
Case Study 2: Residential Landscaping
A homeowner in Colorado installed a cantilever retaining wall to create a terraced garden. The wall not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of the property but also prevented soil erosion during heavy snowmelt.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Cantilever retaining walls are an excellent choice for projects requiring stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Their versatility and efficiency make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from highway construction to residential landscaping.
If you found this article helpful, please share it with others who might benefit from this information. For more insights into civil engineering and construction, explore our other articles on related topics. Feel free to leave a comment below if you have any questions or need further clarification!
Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Calista Greenfelder Jr.
- Username : alba.nienow
- Email : annalise92@armstrong.com
- Birthdate : 1980-07-25
- Address : 386 Gabe Union North Jennifer, ID 19167-1282
- Phone : 1-260-942-5899
- Company : Fay Group
- Job : Shoe Machine Operators
- Bio : Harum vero odio harum quos. Nemo sint velit praesentium enim. Earum quidem officia est.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/thielm
- username : thielm
- bio : Eum commodi velit commodi omnis tempore voluptatum omnis aspernatur.
- followers : 2926
- following : 957
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/melyna_real
- username : melyna_real
- bio : Error aut omnis iste quam. Nostrum excepturi accusamus facere. Vel itaque omnis adipisci maiores dicta facere.
- followers : 1004
- following : 1150
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@melyna_thiel
- username : melyna_thiel
- bio : Omnis consequatur dolor consequatur non.
- followers : 2107
- following : 337
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/mthiel
- username : mthiel
- bio : Magni ut dolore consequuntur vitae atque. Quo officia iste odit quia. Dolor eaque nulla et sed.
- followers : 1948
- following : 2456